The glass atomization core is an atomization core that uses glass material as the base and combines a thin metal layer to achieve heating . From the perspective of technical processes , there are porous glass, glass ball sintering, TGV , etc. Among them , the glass atomization core of TGV process has the advantages of safety, controllable oil supply , and uniform heating . It has been mass - produced on CBD atomizers .
1. Analysis of glass atomization core
Glass is an amorphous solid with silicon dioxide as the main component, which is formed by high-temperature melting and rapid cooling . Therefore , one of the appearance characteristics of the glass atomizer core is that it is transparent or translucent . Take the T G V glass atomizer core as an example . The main component is borosilicate glass , which presents a high transparency effect .

The T G V glass atomizer core is similar to the one shown in the picture.
In the ceramic atomizer core, a certain proportion of glass powder is usually added to optimize the formulation process. The glass powder melts into a liquid phase at high temperature during the firing process, bonding the powders to each other, so that the fired atomizer core has a certain strength . However, since the ceramic core is a multi-component composite system , such as corundum, diatomaceous earth , zirconium oxide, etc., the ceramic atomizer core usually appears white , gray or black .

In terms of technology , porous glass is similar to ceramic core technology , and is prepared by pore-forming method. Pore-forming agents such as paraffin wax are also added to some ceramic components for modification. The general process is : mixing - compression molding - sintering and debinding - cleaning . This is also the understanding of most people about glass atomization cores . The main disadvantages are different pore sizes and easy impurities .
Glass ball sintering uses hollow glass microspheres as pore -forming agents . The difference from conventional porous glass is that the pore size is uniform and there is less residue , but the disadvantage is the high cost .
The porous glass atomizer core that needs to be sintered does not have obvious advantages over the ceramic atomizer core , so it has not entered the mass production stage . The development of T G V process technology has brought new opportunities for glass atomizer cores .
2. TGV process analysis
The TGV (Through Glass Via) process is a technology for making vertical interconnected through holes on a glass substrate. It can achieve through holes with a diameter of less than 10μm and is mainly used in advanced packaging, radio frequency (RF), MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) and optoelectronic integration.
1. What is TGV metallization?
TGV metallization, in simple terms, is a technology that creates tiny through holes on a glass substrate and fills these through holes with metal to achieve electrical connection and signal transmission. Glass substrates have advantages such as good electrical insulation, thermal stability, and a low dielectric constant, making them very suitable for use in electronic devices. By achieving through-hole metallization on a glass substrate, it is possible to provide efficient interconnection channels for electronic components such as chips, greatly improving the performance of electronic devices.
2. TGV metallization process steps
Glass substrate selection and processing : First, we need to select the appropriate glass material, such as high-quality borosilicate glass or quartz glass, which have low thermal expansion coefficient and high dielectric properties. After selection, the glass substrate needs to be carefully cleaned and pre-processed to ensure that its surface is clean and free of defects, laying a good foundation for subsequent processes.
Through-hole production : There are many micro-machining technologies available for this step, such as sandblasting, ultrasonic drilling, wet etching, deep reactive ion etching (DRIE), photosensitive etching, laser etching, etc. Among them, laser induced deep etching (LIDE) is a more advanced method, which can accurately control the aperture size and high aspect ratio through-hole structure, while keeping the sidewall smooth and reducing cracks and roughness.
Seed layer deposition : A very thin metal seed layer is deposited on the inner wall of the glass through hole, usually using a sputtering process. The role of this seed layer is to provide a basis for the attachment of copper or other conductive materials during subsequent electroplating, just like sowing seeds on the land to prepare for subsequent growth.
Filling with conductive materials : Conductive materials such as copper are filled into the prepared through-holes through the electroplating process to form a vertically interconnected conductive path. This process must ensure that the through-holes are completely filled without voids, otherwise the electrical performance will be affected. In large-scale production, it is necessary to precisely control the parameters of electroplating, such as current density, electroplating time, etc., to ensure that each through-hole can be filled with metal with high quality.
Planarization and film removal : After electroplating, the surface needs to be treated with chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) to remove excess metal and make the substrate surface flat. After that, the relevant protective film needs to be removed. A flat surface is conducive to subsequent circuit connection and packaging processes, just like when building a house, the ground needs to be leveled first.
Rewiring and packaging connection : Create a redistribution layer (RDL) on the glass substrate to perform circuit layout and pin design for connection with other chips or external packaging components. Then add bumps or other interconnect structures, such as solder balls, to complete the electrical and mechanical connection between chips. This step is like building a transportation network to connect various electronic components and enable them to work together.
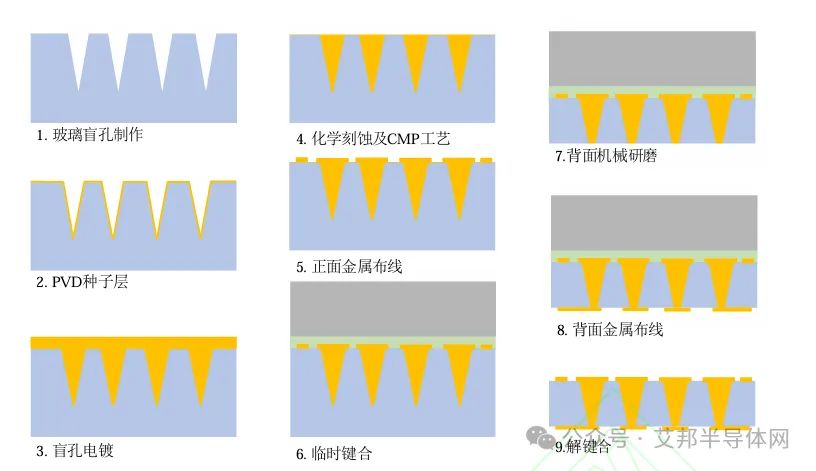
Single-sided blind hole electroplating TGV metallization process Source: Research Progress on RF Integrated Application of Through-Glass Via Technology (Yu Tian et al.)
3. Application of glass atomization core
The Quantum Chip™ , an atomizer core technology launched by Greentank, a CBD atomizer brand, in August 2024 , has attracted the attention of the industry . It uses a proprietary nano - microchip design and advanced microfluidic technology to atomize liquid , which can eliminate harmful and potentially harmful components (HPHC) emissions and flavor degradation generated during thermal cycles . This is considered a typical application of T G V glass atomizer cores .
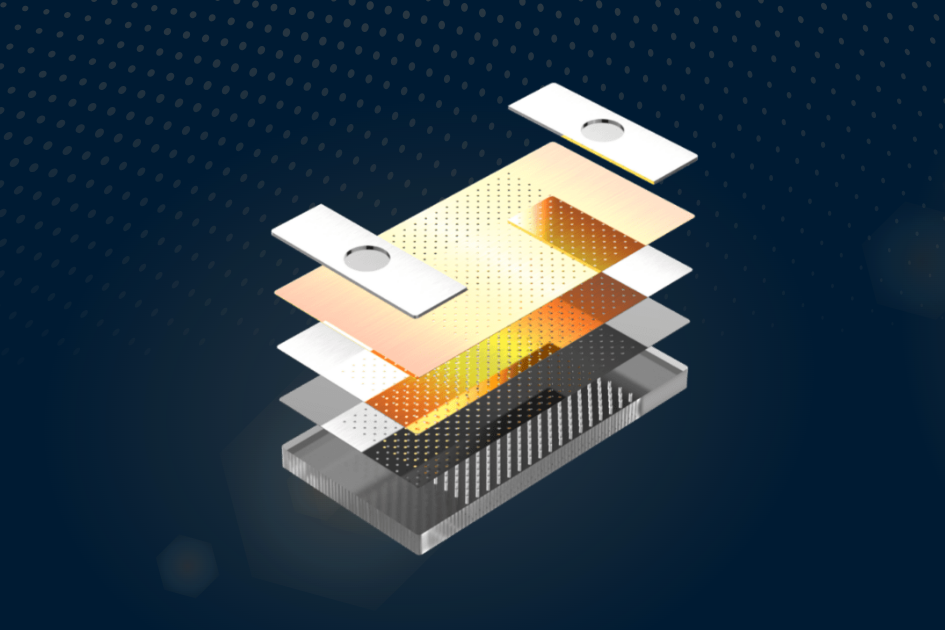
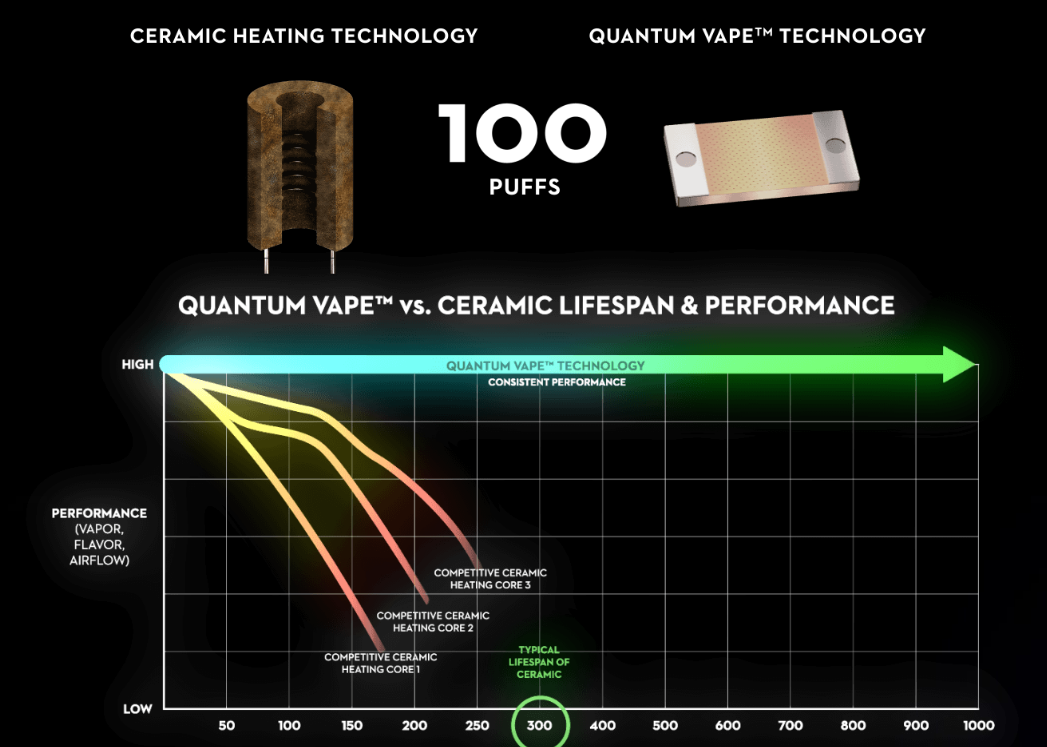
Glass atomizer cores are developing rapidly. Safety, no harmful substances residue, and uniform heating are its advantages, but oil leakage is a challenge. The solution can be to consider reducing the aperture of the through hole, which requires cooperation with laser through-hole equipment, materials and other links.
电子雾化与HNB产品都是新型电子产品,结构虽小,却融合应用多种材料、表面处理、芯片电子等技术工艺,而且雾化技术一直在不断更迭,供应链在逐步完善,为了促进供应链企业间有一个良好的对接交流,艾邦搭建产业微信群交流平台,欢迎加入;Vape e-cigarettes (VAPE) and Heat-Not-Burn e-cigarettes (HNB) are both emerging electronic products. Despite their compact size, they integrate various materials, surface treatment technologies, chip electronics, and other advanced technical processes. Moreover, atomization technology is constantly evolving and the supply chain is being progressively perfected. To facilitate good communication and networking among supply chain enterprises, Aibang has established an industry WeChat group communication platform and warmly welcomes interested enterprises to join.

